📋 Table des Matières
- Introduction
- Installation
- Configuration Rapide
- Fonctionnalités Principales
- Guide d’Utilisation Détaillé
- API Référence
- Exemples Complets
- Dépannage
- Best Practices
🚀 Introduction
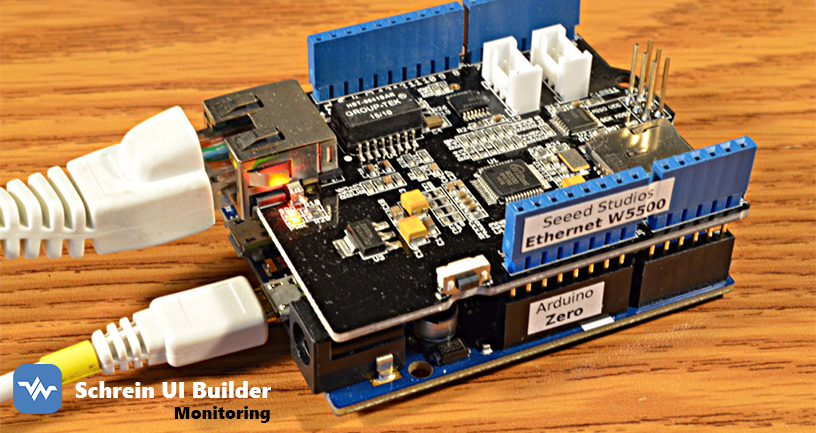
La bibliothèque SchreinEthernetParser est une solution complète pour la communication Ethernet sur Arduino, supportant à la fois les modes client et serveur avec un système de parsing de trames avancé.
Caractéristiques Principales
- Communication TCP/IP en mode client et serveur
- Parsing automatique des trames avec format personnalisé
- Gestion automatique de la reconnexion
- Système de checksum pour l’intégrité des données
- Gestion multi-clients intégrée
- Callbacks événementielles complètes
- Diagnostic et monitoring avancés
📥 Installation
Prérequis
- Carte Arduino compatible Ethernet (Uno, Mega, etc.)
- Shield Ethernet W5100/W5500
- IDE Arduino 1.8.x ou supérieur
Installation de la Bibliothèque
- Téléchargez les fichiers
.het.cpp - Créez un dossier
SchreinEthernetParserdans votre dossierlibraries/Arduino - Copiez les fichiers dans ce dossier
- Redémarrez l’IDE Arduino
⚡ Configuration Rapide
Mode Client (Connexion à un serveur)
#include <SchreinEthernetParser.h>
SchreinEthernetParser ethernet;
byte mac[] = { 0xDE, 0xAD, 0xBE, 0xEF, 0xFE, 0xED };
IPAddress serverIP(192, 168, 1, 100);
uint16_t serverPort = 8080;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
// Initialisation Ethernet
if (ethernet.begin(mac)) {
ethernet.initAsClient(serverIP, serverPort);
}
}
void loop() {
ethernet.loop();
if (ethernet.isFrameAvailable()) {
String value = ethernet.getValue("sensor", "temperature");
if (value != "") {
Serial.println("Température: " + value);
}
}
}Mode Serveur (Attente de connexions)
#include <SchreinEthernetParser.h>
SchreinEthernetParser ethernet;
byte mac[] = { 0xDE, 0xAD, 0xBE, 0xEF, 0xFE, 0xED };
uint16_t serverPort = 8080;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
if (ethernet.begin(mac)) {
ethernet.initAsServer(serverPort);
}
// Configuration des callbacks
ethernet.onNewClient([](IPAddress ip, uint16_t port) {
Serial.print("Nouveau client: ");
Serial.println(ethernet.ipToString(ip) + ":" + String(port));
});
}
void loop() {
ethernet.loop();
}🎯 Fonctionnalités Principales
1. Format des Trames
La bibliothèque utilise un format de trame spécifique :
<[controlName|key|value]&CHECKSUM>Exemple :
<[sensor|temperature|23.5]&A7>2. Gestion Automatique des Connexions
- Reconnexion automatique en cas de déconnexion
- Monitoring de la qualité de connexion
- Nettoyage automatique des clients inactifs
3. Système de Checksum
Vérification d’intégrité des données avec XOR checksum :
ethernet.enableChecksum(true); // Activé par défaut4. Multi-clients
Jusqu’à 10 clients simultanés en mode serveur.
📖 Guide d’Utilisation Détaillé
Initialisation Ethernet
// Configuration DHCP
ethernet.begin(mac);
// Configuration IP statique
IPAddress ip(192, 168, 1, 177);
IPAddress dns(8, 8, 8, 8);
IPAddress gateway(192, 168, 1, 1);
IPAddress subnet(255, 255, 255, 0);
ethernet.begin(mac, ip, dns, gateway, subnet);Envoi de Données
// Création d'une commande
String command = SchreinEthernetParser::command("relay", "state", "on");
// Envoi simple
ethernet.sendFrame(command);
// Envoi multiple
String frames[] = {
SchreinEthernetParser::command("sensor1", "temp", "22.5"),
SchreinEthernetParser::command("sensor1", "hum", "45.0")
};
ethernet.sendFrames(frames, 2);Réception de Données
void loop() {
ethernet.loop();
if (ethernet.isFrameAvailable()) {
String temp = ethernet.getValue("sensor", "temperature");
String hum = ethernet.getValue("sensor", "humidity");
if (temp != "") {
Serial.println("Température: " + temp);
}
if (hum != "") {
Serial.println("Humidité: " + hum);
}
ethernet.markFrameAsProcessed();
}
}Callbacks Événementielles
void setup() {
// Nouveau client connecté
ethernet.onNewClient([](IPAddress ip, uint16_t port) {
Serial.println("Nouvelle connexion: " + ethernet.ipToString(ip));
});
// Données reçues
ethernet.onDataReceived([](const String &data, IPAddress senderIP, uint16_t senderPort) {
Serial.println("Données brutes: " + data);
});
// Trame parsée
ethernet.onFrameParsed([](const String &controlName, const String &key, const String &value) {
Serial.println(controlName + " - " + key + ": " + value);
});
// Erreur
ethernet.onError([](const String &error) {
Serial.println("Erreur: " + error);
});
}🔧 API Référence
Méthodes Principales
| Méthode | Description |
|---|---|
begin() | Initialise la connexion Ethernet |
initAsClient() | Configure en mode client |
initAsServer() | Configure en mode serveur |
loop() | Boucle principale à appeler régulièrement |
sendFrame() | Envoie une trame |
getValue() | Récupère une valeur parsée |
Gestion Connexion
| Méthode | Description |
|---|---|
isConnectionHealthy() | Vérifie l’état de la connexion |
getConnectionStatus() | Statut détaillé de la connexion |
forceReconnect() | Force une reconnexion |
getConnectionQuality() | Qualité de connexion (0-100%) |
Diagnostic
| Méthode | Description |
|---|---|
debugOutput() | Sortie de diagnostic |
getClientCount() | Nombre de clients connectés |
getMacAddress() | Adresse MAC de la carte |
Callbacks
| Callback | Déclenchement |
|---|---|
onNewClient | Nouveau client connecté |
onDataReceived | Données brutes reçues |
onFrameParsed | Trame correctement parsée |
onError | Erreur détectée |
💡 Exemples Complets
Exemple 1: Station Météo
#include <SchreinEthernetParser.h>
SchreinEthernetParser ethernet;
byte mac[] = { 0xDE, 0xAD, 0xBE, 0xEF, 0xFE, 0xED };
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
if (ethernet.begin(mac)) {
ethernet.initAsServer(8080);
}
ethernet.onFrameParsed(handleParsedFrame);
}
void handleParsedFrame(const String &controlName, const String &key, const String &value) {
if (controlName == "weather" && key == "temperature") {
float temp = value.toFloat();
Serial.print("Température: ");
Serial.println(temp);
// Envoi d'un accusé de réception
String ack = SchreinEthernetParser::command("ack", "temp", "received");
ethernet.sendFrame(ack);
}
}
void loop() {
ethernet.loop();
}Exemple 2: Contrôleur Domotique
#include <SchreinEthernetParser.h>
SchreinEthernetParser ethernet;
byte mac[] = { 0xDE, 0xAD, 0xBE, 0xEF, 0xFE, 0xED };
IPAddress serverIP(192, 168, 1, 100);
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
if (ethernet.begin(mac)) {
ethernet.initAsClient(serverIP, 8080);
}
pinMode(13, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
ethernet.loop();
if (ethernet.isFrameAvailable()) {
String ledState = ethernet.getValue("control", "led");
if (ledState == "on") {
digitalWrite(13, HIGH);
// Confirmation
ethernet.sendFrame(SchreinEthernetParser::command("status", "led", "on"));
} else if (ledState == "off") {
digitalWrite(13, LOW);
ethernet.sendFrame(SchreinEthernetParser::command("status", "led", "off"));
}
ethernet.markFrameAsProcessed();
}
// Envoi périodique de données de capteur
static unsigned long lastSend = 0;
if (millis() - lastSend > 5000) {
int sensorValue = analogRead(A0);
String sensorFrame = SchreinEthernetParser::command("sensor", "value", String(sensorValue));
ethernet.sendFrame(sensorFrame);
lastSend = millis();
}
}🔍 Dépannage
Diagnostic Complet
void checkStatus() {
// Statut Ethernet détaillé
Serial.println(ethernet.debugOutput("ethernetStatus"));
// Clients connectés
Serial.println(ethernet.debugOutput("clients"));
// Dernière erreur
Serial.println(ethernet.debugOutput("error"));
// Statistiques connexion
Serial.println(ethernet.debugOutput("connectionStats"));
}Problèmes Courants
- Carte Ethernet non détectée
// Vérifier le câblage et l'alimentation
Serial.println(ethernet.debugOutput("ethernetStatus"));2. Déconnexions fréquentes
// Activer le monitoring de qualité
ethernet.onConnectionQualityUpdate([](int quality) {
Serial.println("Qualité connexion: " + String(quality) + "%");
});3. Trames non reçues
// Vérifier le format des trames
ethernet.onDataReceived([](const String &data, IPAddress ip, uint16_t port) {
Serial.println("Donnée brute: " + data);
});Codes d’Erreur
| Code | Description |
|---|---|
NO_ERROR | Aucune erreur |
BUFFER_OVERFLOW | Buffer de réception plein |
INVALID_FRAME | Trame mal formée |
TIMEOUT | Timeout réception |
CHECKSUM_ERROR | Checksum invalide |
ETHERNET_DISCONNECTED | Carte Ethernet déconnectée |
💡 Best Practices
1. Gestion des Erreurs
void setup() {
ethernet.onError([](const String &error) {
Serial.println("ERREUR: " + error);
// Tentative de reconnexion automatique
if (ethernet.getConnectionQuality() == 0) {
ethernet.forceReconnect();
}
});
}2. Performance et Mémoire
// Réduire la taille des buffers si nécessaire
#define BUFFER_SIZE 128
#define MAX_FRAME_SIZE 128
// Nettoyer régulièrement
void loop() {
ethernet.loop();
ethernet.cleanupClients(30000); // 30 secondes timeout
}3. Sécurité
// Validation des données reçues
void handleData(const String &controlName, const String &key, const String &value) {
if (controlName.length() > 20 || key.length() > 20) {
Serial.println("Trame suspecte rejetée");
return;
}
// Traitement sécurisé...
}4. Monitoring Avancé
void monitorSystem() {
Serial.println("=== STATUT SYSTÈME ===");
Serial.println("IP: " + ethernet.ipToString(ethernet.getLocalIP()));
Serial.println("Clients: " + String(ethernet.getClientCount()));
Serial.println("Statut: " + ethernet.getConnectionStatus());
Serial.println("Qualité: " + String(ethernet.getConnectionQuality()) + "%");
Serial.println("MAC: " + ethernet.getMacAddress());
}📞 Support
Ressources Utiles
- Documentation technique : Référence API complète
- Exemples : Dossier d’exemples fourni
- Debugging : Utilisez
debugOutput()pour le diagnostic
Journalisation
Activez les logs série pour le débogage :
Serial.begin(115200); // Haut débit pour les logsCette documentation couvre l’ensemble des fonctionnalités de la bibliothèque SchreinEthernetParser. Pour toute question supplémentaire, référez-vous aux exemples fournis et aux commentaires dans le code source.